SELinux is a Linux kernel security implementation that allows system administrators to have more control over the system. It was originally developed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA) as a series of patches to the Linux kernel using Linux Security Modules (LSM).
It provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including MAC (mandatory access controls). The main reasons behind the implementation are to enforce data confidentiality and integrity, as well as to protect processes from untrusted inputs.
Normally, this doesn’t cause a problem unless a foreign file or application is trying to access your system, requiring you to disable SELinux either temporarily or permanently.
In this guide, you will learn how to check the status and then temporarily or permanently disable or enable SELinux in RedHat-based distributions such as CentOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, etc.
How to Check the SELinux Status in Linux
SELinux operates in three global modes: Enforcing mode, in which policy is enforced and logged; Permissive mode, in which policy is not enforced but logged. Disable mode, in which the policy is not loaded and logged.
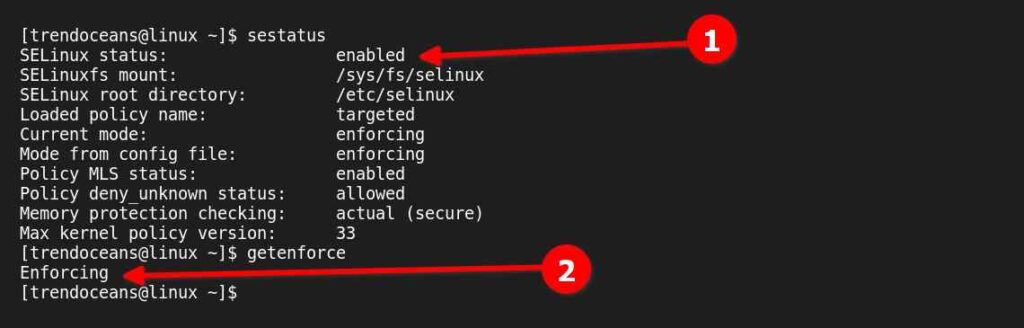
First, check if SELinux is enabled or set to Enforced mode using any of the following commands.
$ sestatus
OR
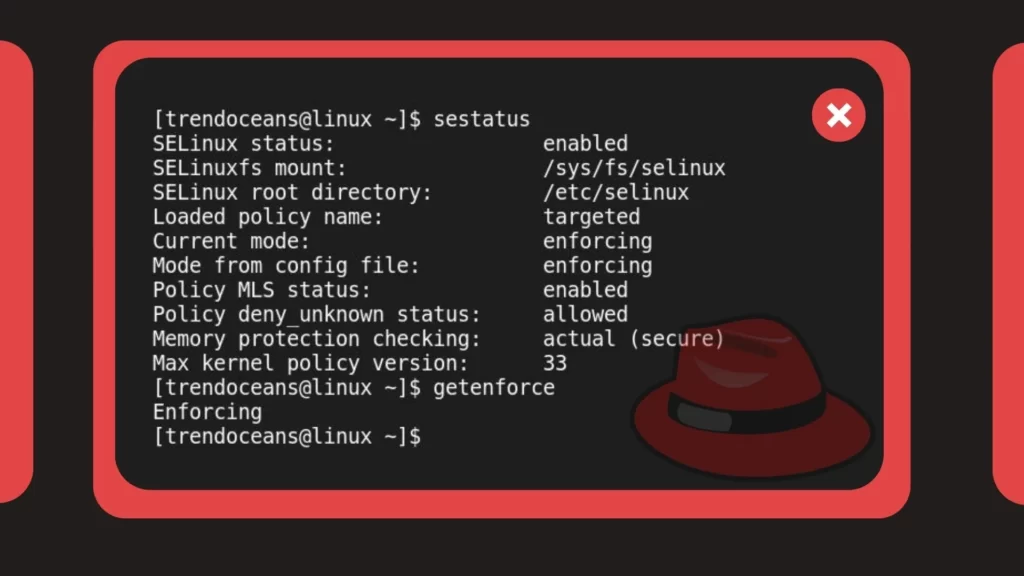
$ getenforce Below is the output of the above commands.
SELinux is currently enabled on my system. Now, we will look at how to disable it temporarily or permanently on our system.
How to Disable SELinux Temporarily in Linux
SELinux can be set to the Permissive mode (disable) temporarily in Linux using any of the following commands.
$ sudo setenforce 0
OR
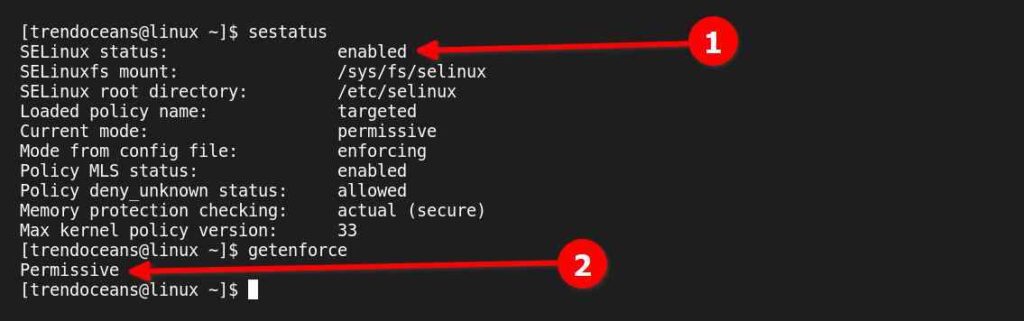
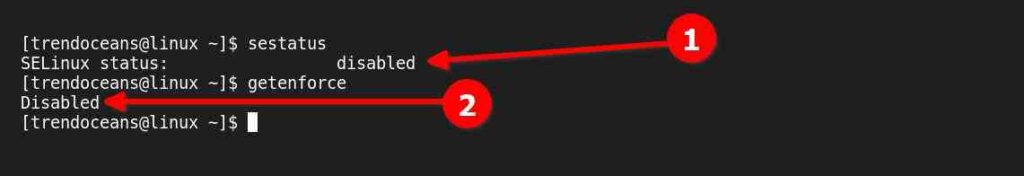
$ sudo setenforce PermissiveThe above methods will maintain the SELinux state to Permissive mode (Disable) until the next reboot. To verify the status execute any of the below commands.
$ sestatus
OR
$ getenforce Below is the output of the above commands.
If you would like to change the status from “Permissive mode” to “Enforced mode” without a reboot, then execute any of the below commands.
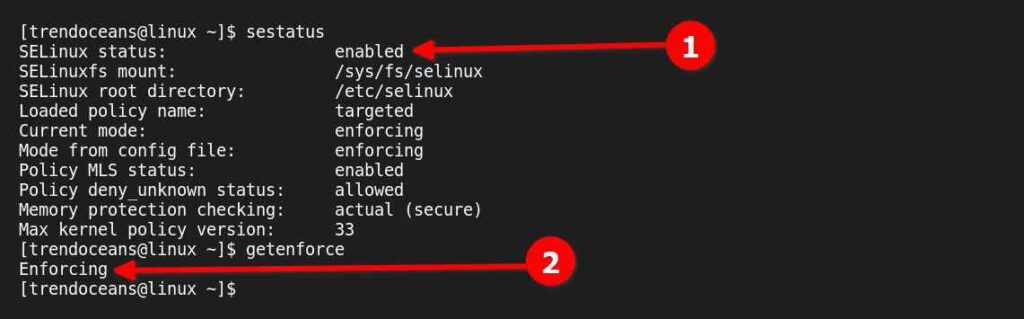
$ sudo setenforce 1
OR
$ sudo setenforce EnforcingTo verify the status, execute any of the below commands.
$ sestatus
OR
$ getenforce Below is the output of the above commands.
How to Disable SELinux Permanently in Linux
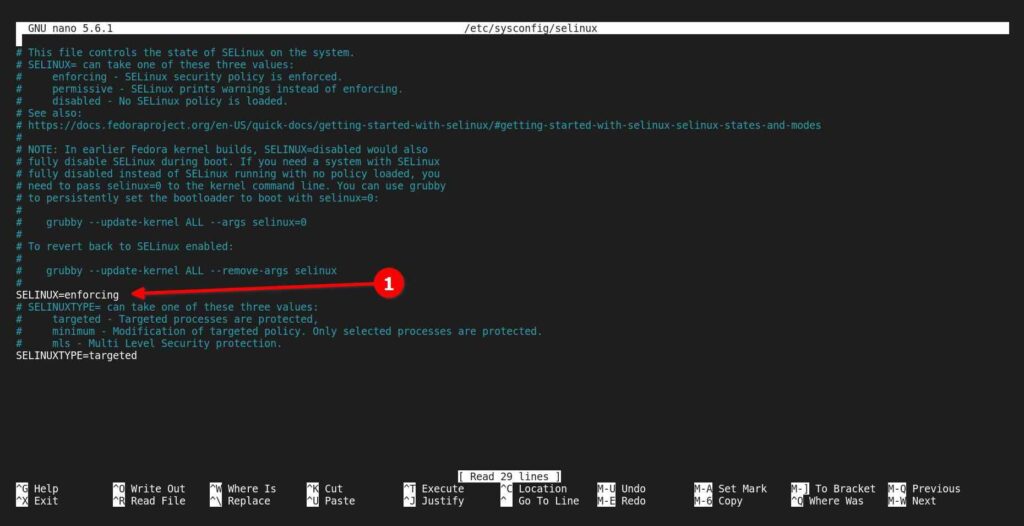
Disabling SELinux permanently is not recommended, although you can edit /etc/sysconfig/selinux to disable it permanently until manually enabled by you.
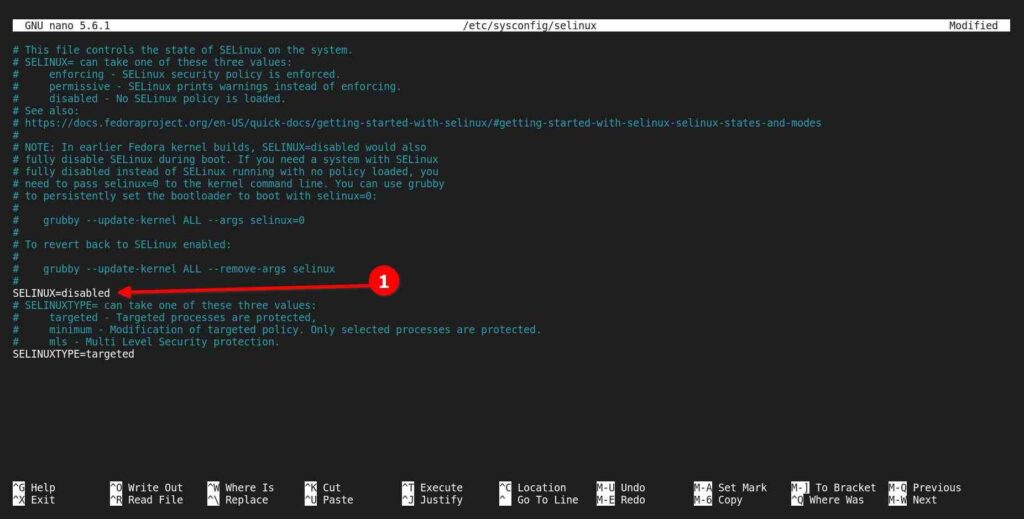
$ sudo nano /etc/sysconfig/selinuxBelow is the output of the above command.
Now change the value of SELINUX=enforcing to SELinux=disabled as shown below.
Finally, save and exit the file, and reboot your system to apply the changes. Then execute any of the below commands to verify the status.
$ sestatus
OR
$ getenforce Below is the output of the above commands.
That’s all you need to know about how to disable the SELinux policy temporarily and permanently. If you have any queries, check the FAQ or feel free to comment.
FAQ
No, the firewall is a mediator between the computer and the network and monitors the flow of traffic. whereas SELinux uses policy to monitor foreign files or applications trying to access your system.
Yes, as an informed Linux user and system administrator, it is important to learn and use SELinux.
Ubuntu offers AppArmor as an alternative to SELinux.