Nginx is an open-source lightweight web server alternative to apache to handle high-traffic websites.
With all its due features, it can easily manage to load balance and reverse proxy for your site or can be used as a mail server proxy as a POP and IMAP.
By default, Nginx runs on port 80 to handle web traffic requests, which can be changed to something else by editing the configuration files.
Today, you will learn how to change the Nginx port in Linux in a few simple steps.
Prerequisites
- Nginx Web Server in your system
- Web Browser to check the result (Chrome, Firefox, etc.)
- Your 2-minute time
How to Install Nginx in Linux (Skip if it exists)
To install the Nginx web server for your Debian or RHEL-based distributions, ensure you have a proper internet connection and open your terminal using Ctrl+Alt+t or Ctl+Shift+t and execute the below command.
Note: Installation requires system changes, having a root user or sudo account should be a must to gain the privileges.
$ sudo apt install nginx [On Debian/Ubuntu]
$ sudo dnf install nginx [On CentOS/Fedora]After the installation process is complete, start the server daemon process using the below command.
$ sudo systemctl start nginxAs you have installed Nginx in your respective Linux system, you can jump to the next step to continue changing the Nginx port in Linux.
Modifying the Configuration Files
Changing the default Nginx port requires modifications in the configuration files. This configuration file location might differ from distribution to distribution.
For Debian/Ubuntu distributions, the Nginx Web Server configuration file required to be modified is located at /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
For CentOS/Fedora distributions, the Nginx Web Server configuration file required to be modified is located at /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Change Nginx Port in Linux
Before starting the process of changing the default port, stop your currently running server using the below command.
$ sudo systemctl stop nginxVerify the process is stopped using the below command.
$ systemctl status nginxTo change the default port (80) for HTTP, modify the below Nginx configuration file depending on the type of distribution you were using, using the text editor (nano, vim).
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default [On Debian/Ubuntu]
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf [On CentOS/Fedora]Below is the output of the above default and nginx.conf configuration files.
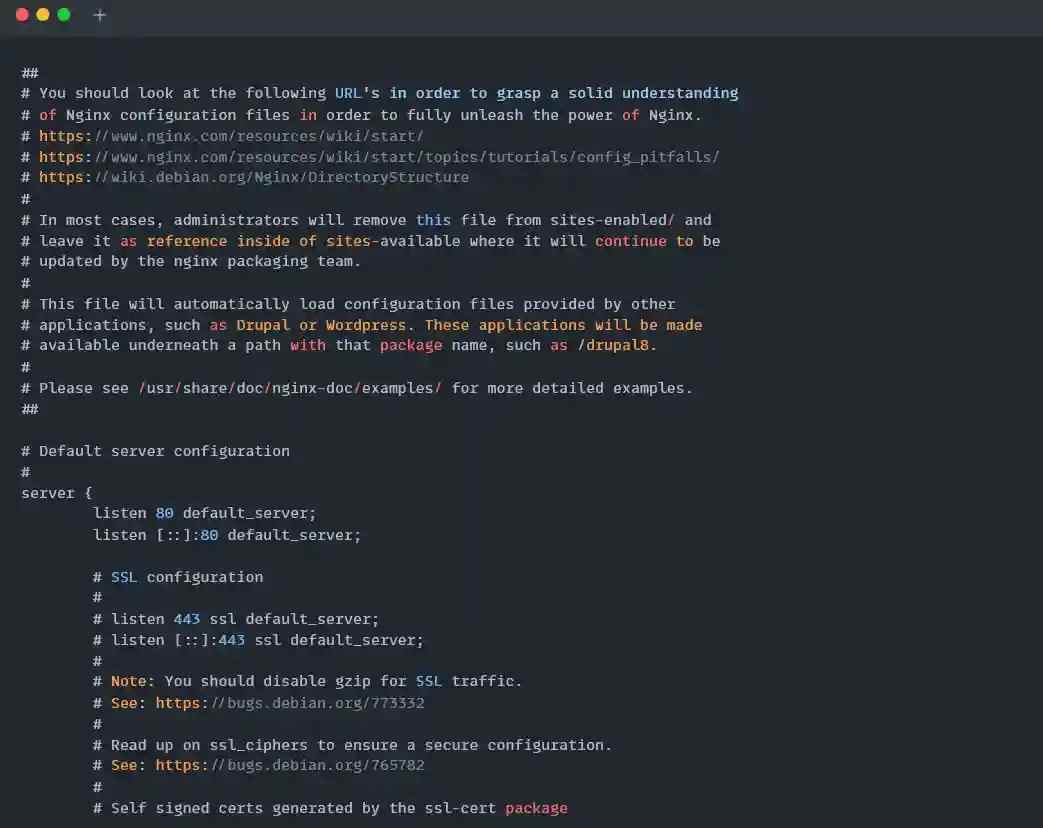
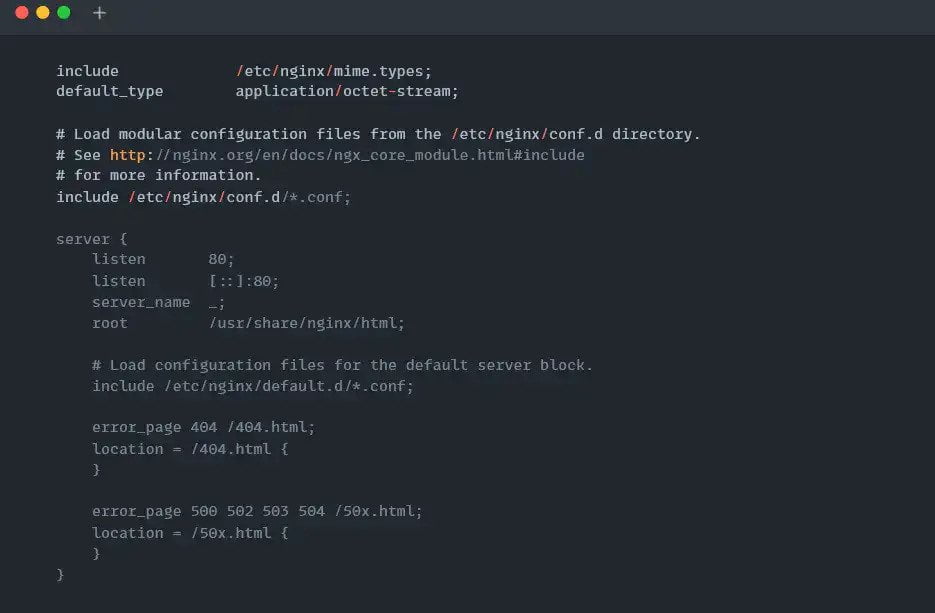
Once the configuration file is opened, find the Listen 80 and Listen [::]: 80 string within the file and replace 80 with something else. For me, it’s 88 port, as shown below.
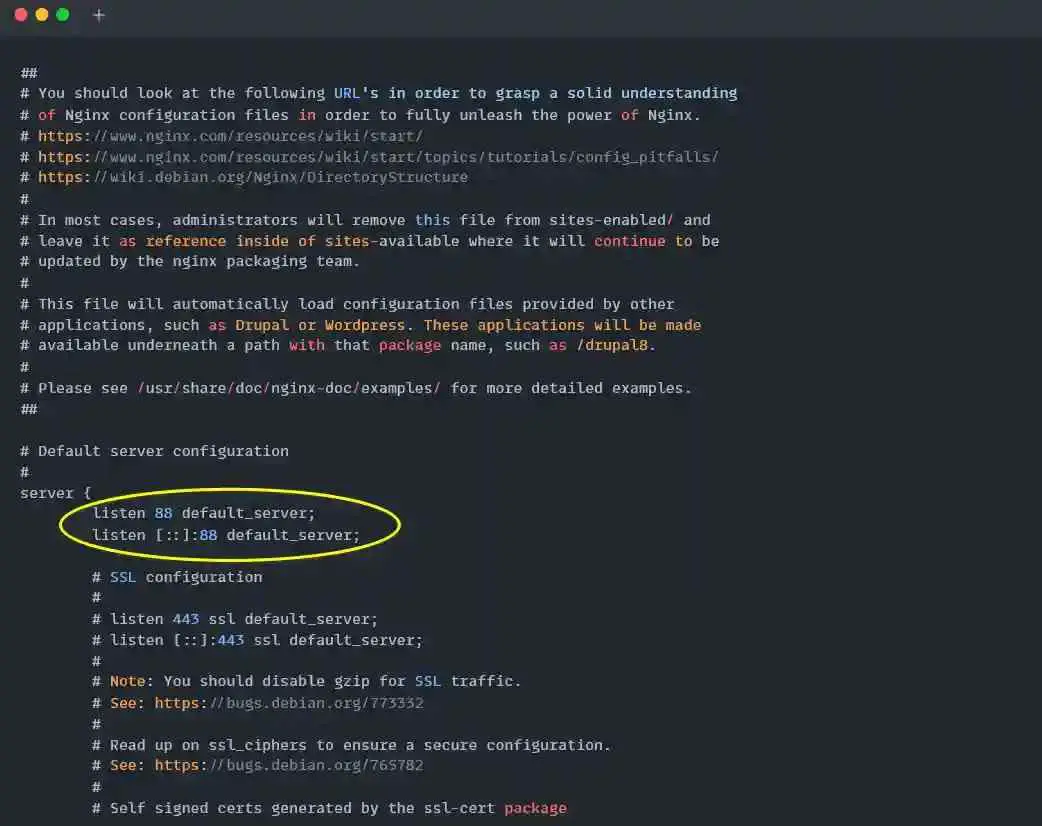
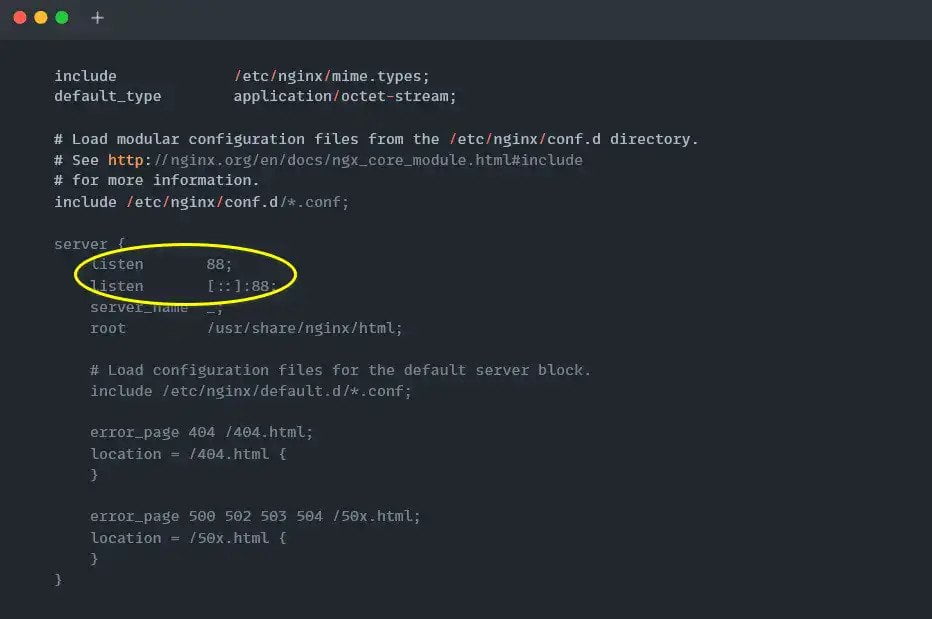
After the configuration is saved with the modification for Debian or Ubuntu-based Distributions, start or restart the Nginx server using the below command.
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx [On Debian/Ubuntu]During assigning port, RHEL-based distributions such as CentOS or Fedora require you to install policycoreutils and add the below rules required by SELinux for nginx.
$ sudo dnf install policycoreutils
$ sudo semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 88
$ sudo semanage port -m -t http_port_t -p tcp 88Finally, restart the Nginx web server to apply changes.
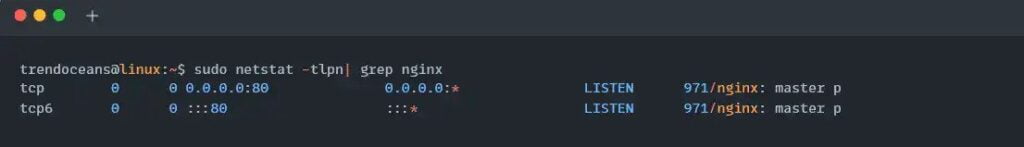
$ sudo systemctl restart nginxNow Nginx is bound to the new port 88. You can check your local network socket table using the netstat command to find the Nginx port as listed below.
$ sudo netstat -tlpn| grep nginxBelow is the output of the above command.
Finally, open your Web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) and enter http://localhost:88.
Suggestion for you :How to Change Apache HTTP Port in Linux