Gparted is a Graphical tool to manage Disk Partition. It is also one of the best tools to manage Disk. You can create Partition, Format, and many more.
In this guide, we will show you how to install GParted on all major Linux Distribution. Whether you are using ubuntu or arch, we give a complete guide for all Distribution.
How to Install GParted on Linux
Gparted is not preinstalled on Linux Distribution So, we need first to install GParted. We can easily Install GParted using the following command for the different distributions.
Before that make sure to update official repository.
Installing Gparted on Ubuntu/Debian
$ sudo apt install gpartedInstalling Gparted on Centos/RHEL/Fedora
$ sudo yum install gpartedInstalling Gparted on ArchLinux
$ sudo pacman -Sy gparted"Installing GParted on Opensuse
$ sudo zypper install gpartedHow to use Gparted
We have successfully Installed gparted on Our System. Now it’s time to explore gparted in depth.
You can run GParted for the terminal as well as from the App Manager, and Gparted requires sudo access to use.
To run type the command
$ gparted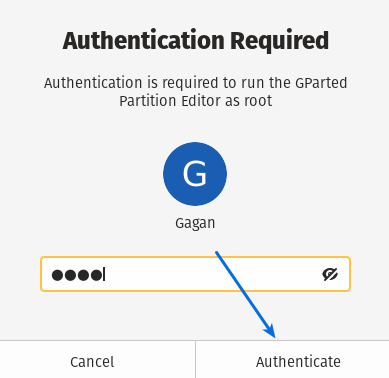
Now enter the root password and click on Authenticate to use gparted. Wait for a second to start gparted.
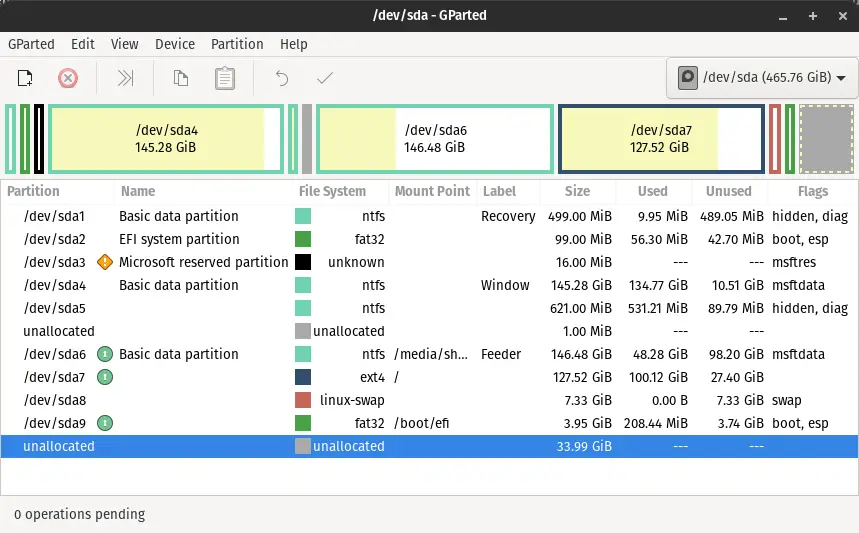
Explore Gparted
When the gparted start, you will see the number of Options such as partition, Name, Filesystem, Mount Point, Label Size, Used space, Unused Space, and flags.
You can see the partition size in various colors with the size of the disk and partition name.
We will explore every option in detail. First started with Selecting the attached Storage device.
Select attached Storage Device
When you have more than 1 hard disk or any storage device to explore the attached disk, click on the drop-down menu option, and you will able to see all the storage disks.
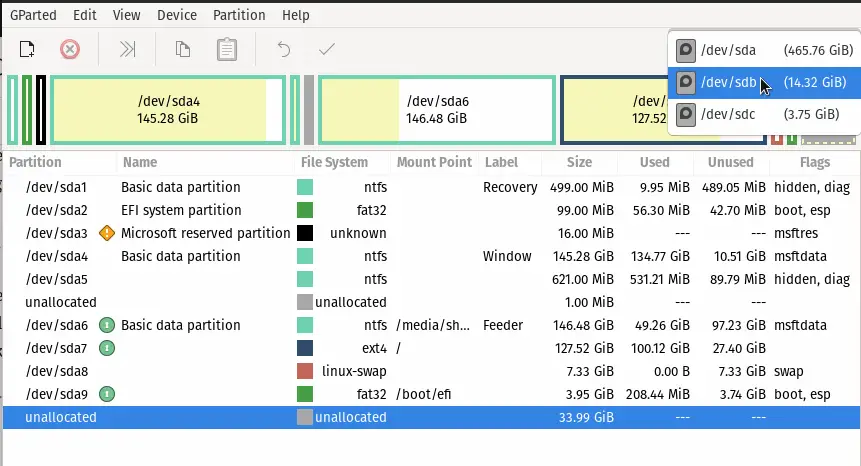
If you have connected your external hard disk or USB drive to your system and still the device is not showing in the drop menu?
Press the Ctrl + R or Click on the Gparted menu option, which is on the top left side menu, and Click on Refresh Devices.
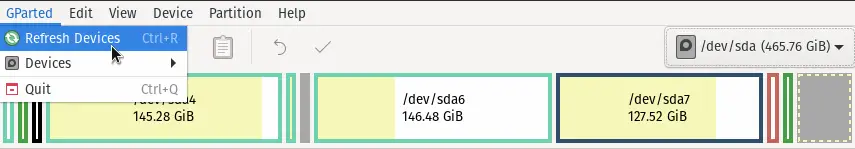
After this, again click on the drop-down menu options, and you will able to see other attached storage devices.
Format disk or partition using Gparted
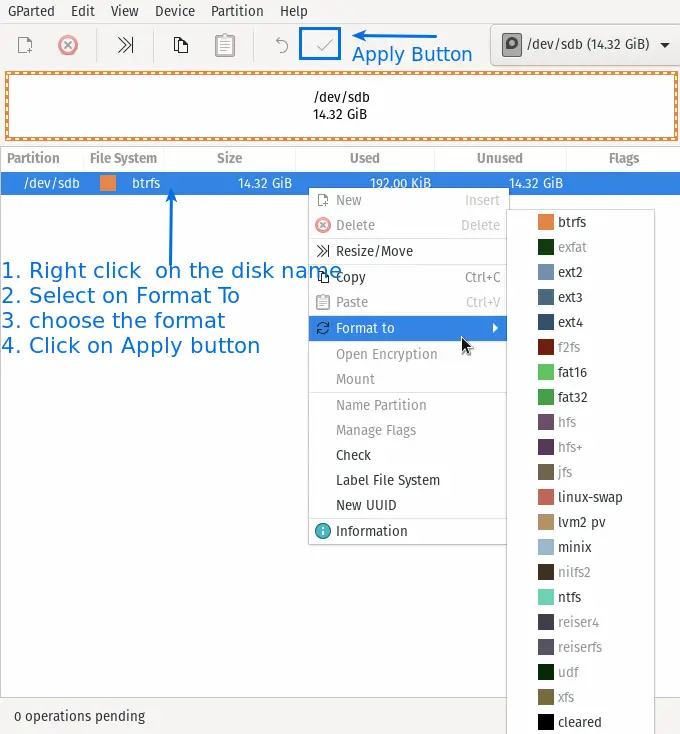
In this step, we will format partition or disk /dev/sdb to fat32, which is currently in the btrfs file system.
To format a partition, you need to right-click on the partition name and go to the option Format to, select the partition you want for your disk.
In my case I want my disk format to be fat32 So, I have selected fat32 now click on the Apply Button.
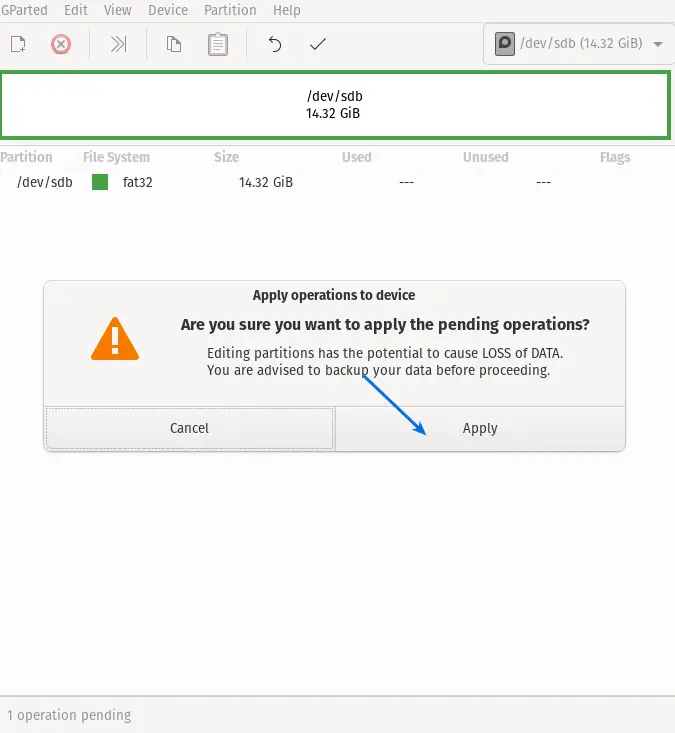
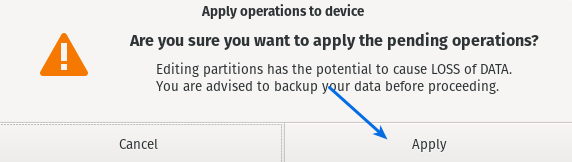
It will ask for your consent, and this procedure will completely wipe your data. If you want to proceed, then click on Apply.
This process will take some time to complete, and it depends upon the size of the disk and file already stored.
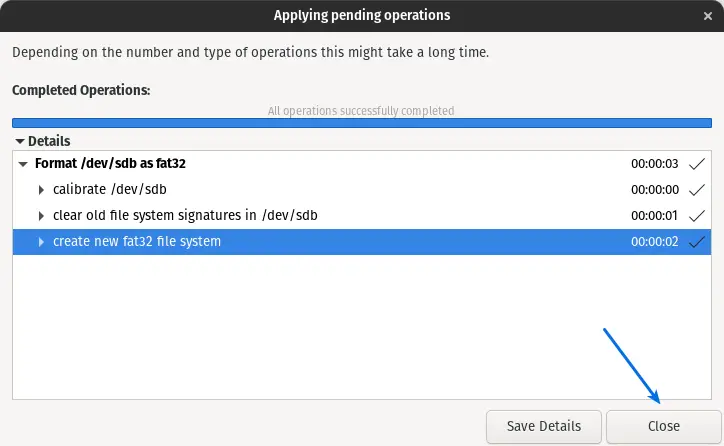
You will get the confirmation “All Operations successfully completed”.To check, click on close.
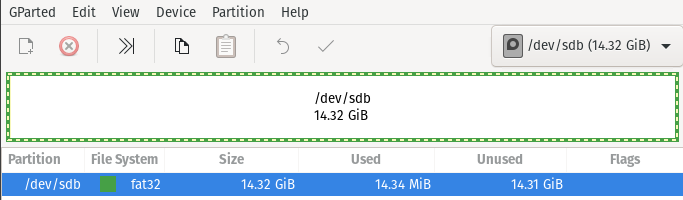
Now you can see Disk is formatted to as per the our preference.
Read this:- How to Format USB Drive or Pendrive on Linux?
Create a New Partition Table using Gparted
In this step, we will create a new Partition Table for our Disk “/dev/sdb” and Make sure to select the right Disk; otherwise, and you can lose your data.
To create Partition Table go to the Gparted Menu Options > Device > Create Partition Table

Now you will get the options to select the type of partition table, Select the partition table as per your requirement.
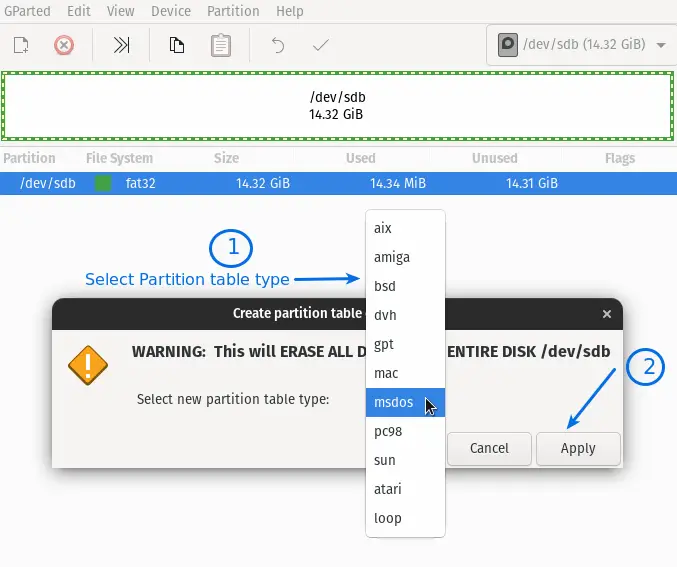
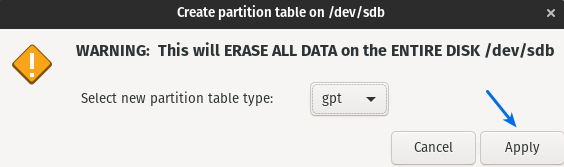
I have selected gpt partition,and last click on the Apply button.
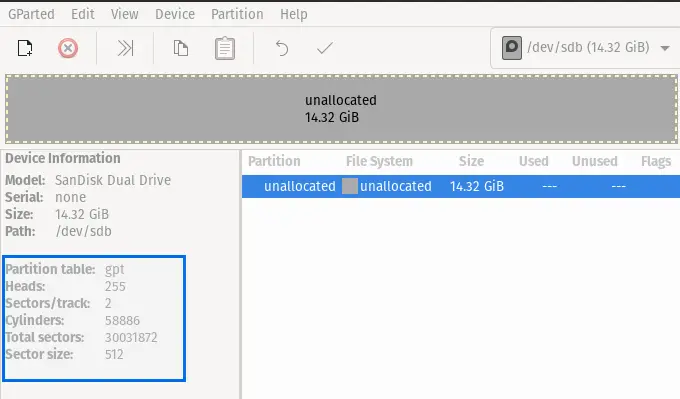
We able to create a gpt partition table to verify go the GParted menu option Click on View > Device Information, and you will get the completed Information about disk
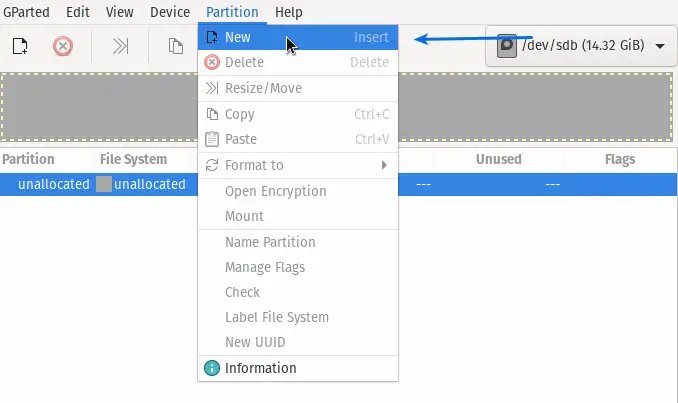
That’s it to create a partition table on gparted. Now we will see how to create a partition.
Create New Partitions Using Gparted
To create a new partition, go the Gparted > Partition > New, or you can right-click on the disk name and select the New option.
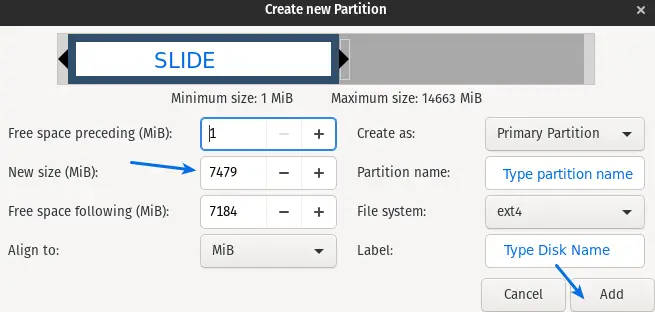
On the next screen, you will get the option to set the size according to your requirement. In the New size (MiB), enter the size of the new partition to calculate. You can multiply like New Size = Required GB * 1024
You can set the File system, partition name, and Label name. After all, click on Add Button.
Click on Apply button to format
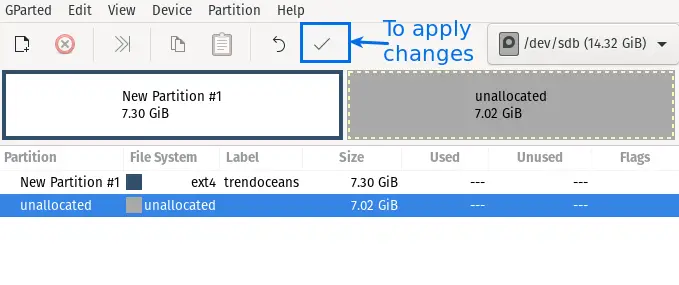
Again click on apply button to see changes
You can see now we have two partitions One partition size is 7.30GB and another 7.02GB, which is unallocated on a 15GB Disk.
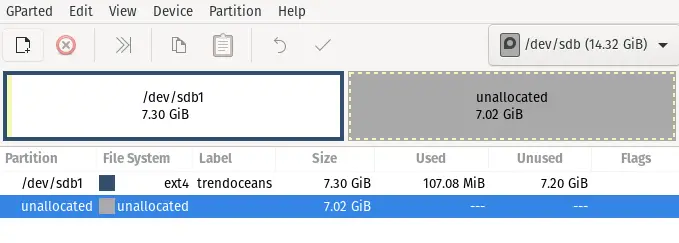
You are able to create a new partition on your disk. Before making a partition, make sure you have the required space available.
Delete partition using Gparted
So far, we able to create a partition table and create a new partition using gparted. Now we delete to create a partition.
To delete a partition, select the partition which you want to delete and press the right-click button, or you can click on the Delete button from the toolbar.
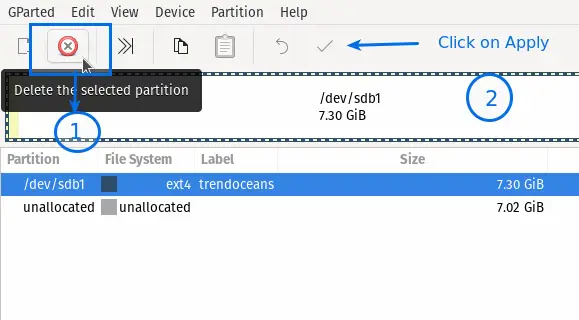
Then click on the Apply button, and wait for some seconds or minutes to delete the partition.
That’s it you are to delete selected partition using Gparted.
I hope so you able to understand how to use Gparted on Linux. If you are facing any kind of issue while using, you can comment to us.
One of the detail blog i ever read. Awesome explaination as well as easy to understand with proper methods!