There is no need to install an SSH server on Fedora 38, and later you just need to enable and start the service by following the steps below.
Once you have installed the Fedora system on your VirtualBox or hardware, there may be a possibility you will access your system remotely through the SSH service, and when you try to access it, you may find the error “ssh: connect to host 192.168.40.120 port 22: No route to host.”
And when you try to check the status of the SSH service in your Fedora, you may get another error: “Unit ssh.service could not be found.”
If you are also facing a similar kind of issue or want to install an SSH server on Fedora, then this article can be helpful to you.
Table of Contents
 Install an SSH Server on Fedora 38 and Later
Install an SSH Server on Fedora 38 and Later
As far as I know, you will find the OpenSSH server preinstalled on your Fedora machine. To get a better idea of whether it is available or not, run the below command, which will print the OpenSSH server version.
$ rpm -iq openssh-server
openssh-server-8.8p1-1.fc36.1.x86_64If you get the output with the OpenSSH version, then you are good to go ahead and enable the SSH service in the next section.
And for those who get the output “OpenSSH version is not installed,” type the below code to start the installation.
$ sudo dnf install openssh-serverOnce the installation is complete, move on to the next part to enable the SSH service.
 Enable the SSH server on Fedora 38 and Later
Enable the SSH server on Fedora 38 and Later
The very first step to resolving the above error is to enable the SSH service on your Fedora system, and you will probably get the above error when you try to start the SSH service.
This error is common among newcomers who have recently switched from Ubuntu to Fedora.
In Ubuntu, when you invoke the below command to start or check the status on your terminal, it gets accepted because the ssh unit service is available and it is mapped to the default sshd.unit service.
$ sudo systemctl status sshd
OR
$ sudo systemctl start sshdAnd this is not the same case with Fedora.
You have to invoke the proper command to enable, start, or stop the SSH service.
To check the SSH service status in Fedora, run the below command:
$ sudo systemctl status sshdThe output of the above command cleared out the error and showed the current status of the OpenSSH service, which is “inactive”.
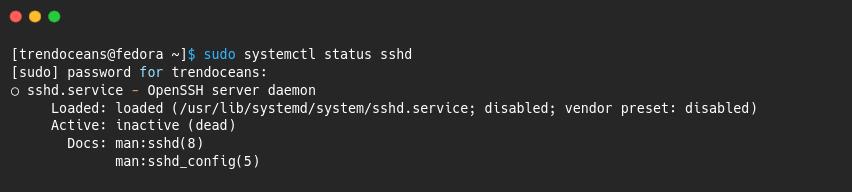
Now you can easily change the status to “active”.
But before doing that, you need to enable the sshd service to automatically restart the SSH service after every boot.
$ sudo systemctl enable sshd Start the OpenSSH Server on Fedora 38 and Later
Start the OpenSSH Server on Fedora 38 and Later
Once you are done with the above step, you can start the SSH service to connect with the remote host system.
Run the below code to start the SSH service to connect with the remote system.
$ sudo systemctl start sshdAfter that, once again, check the current status of the SSH service.
$ sudo systemctl status sshdTry to Connect your Fedora Machine
Once the above changes have been successfully implemented, you can try to connect back to your Fedora system from a remote system.
$ ssh [email protected]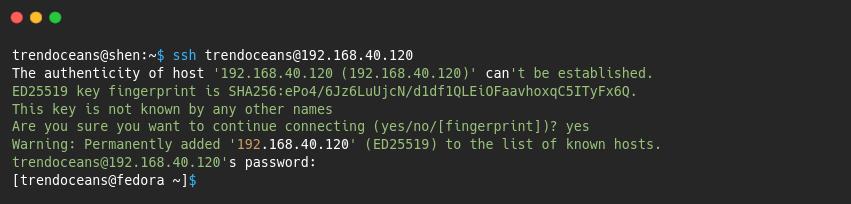
If the firewall is implemented on your system, then run the following line on your Fedora system to accept incoming SSH connections through the firewall connection, and then try to connect to your Fedora system.
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=ssh
# firewall-cmd --reloadThat’s all for this guide, where I showed you how to install, start, and enable an SSH server in Fedora.
As I said above, in Fedora, OpenSSH server is preinstalled; you just need the right command to enable the service, and the commands that we used for this purpose are: sudo systemctl enable sshd and sudo systemctl start sshd
In this particular article, you have learned the following:
- How to install an SSH server in Fedora
- How to start an SSH server in Fedora
- Steps to resolve when SSH server is not working
- How to check SSH service status in Fedora
With this text let me end here.

A man with a tech effusive who has explored some of the amazing technology stuff and is exploring more. While moving towards, I had a chance to work on Android development, Linux, AWS, and DevOps with several open-source tools.
Hi, i did as it’s explained. i’ve got two laptops, one on fedora36 another on fedora 21, i can connect/login ssh in terminal from f21 to f36, but if i try to login from f36 to f21 it says Connection reset by 192.168.0.173 port 22. Could you advise what’s wrong with me?
Hey, First of all, what mechanism do you use to access Fedora 36 to F21, a simple password or a keygen, and second, did you check the firewall rules?