NGINX provides you with many more options than any available web server provides to customize your website for performance, optimization, and security.
So far, you have learned:
- How to allow/restrict access by IP address
- How to create and configure a 404 Error Page
- How to change the Nginx Web Document Location
- How to change the Nginx 80 Port in Linux.
In this article, you are about to learn how to increase the worker process limits, the worker connections, and most importantly, how to prevent the “worker connections are not enough” error on the NGINX web server.
How to Increase the Worker Processes in NGINX?
In layman’s terms, a worker process is a number of cores assigned to your NGINX to handle the traffic. Each worker process (or core) can handle up to 512, 768, or 1024 connections, mostly depending upon your server size.
This value is defined inside the nginx.conf configuration file with the directive worker_processes. By default, the value for this directive is auto.
trendoceans@linux:~$ cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep worker_processes
worker_processes auto;However, you can find the maximum available cores on your server and assign the maximum number of cores to use at all times. But remember, when you assign the maximum number of cores to your NGINX worker process, they are left idle when they are not in use.
It is all your choice. I would personally suggest you go with the auto. However, you can execute the following command to find the maximum number of cores available on your server to be able to assign them to NGINX as a worker process.
trendoceans@linux:~$ grep processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
4As you can see above, 4 is the maximum number of available cores in my system that can be assigned as a worker process.
To assign them, open your NGINX configuration file using your choice of text editor.
trendoceans@linux:~$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/nginx.confUpdate the worker_processes directive value from auto to your maximum number of cores.
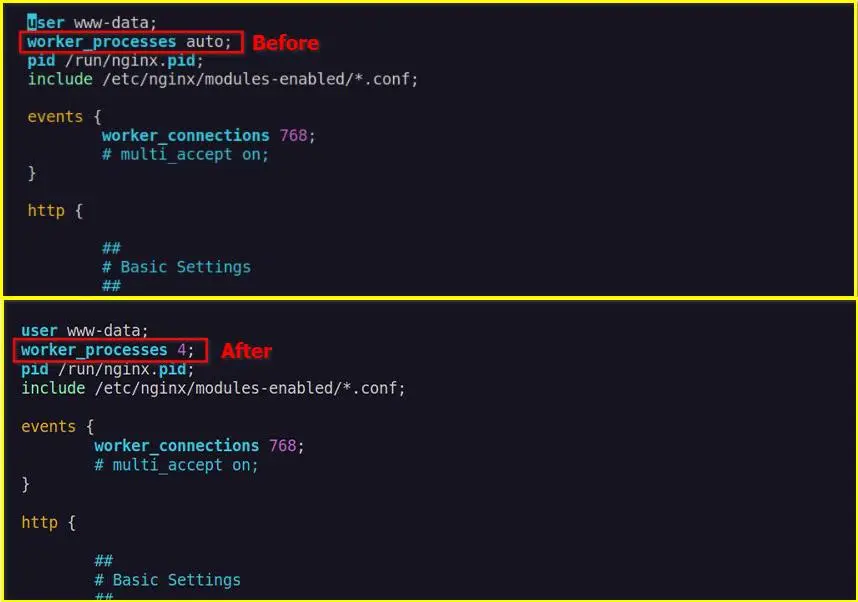
I would still suggest you go with the auto value unless you know what you are doing.
Also Read: GoAccess Tool: Monitor Real-Time Apache and Nginx Server Logs
How to Increase the Worker Connections in NGINX?
The worker connection is the maximum number of clients that can be connected to each worker process (or core). The default values are 512, 768, or 1024 connections, mostly depending upon your server size.
Execute the following command to find your current allocated worker connection value.
trendoceans@linux:~$ cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf | grep worker_connections
worker_connections 768;As you can see above, each worker process (or core) on my server can handle up to 768 worker connections (or clients).
In certain events, when your server reaches its maximum limit and no more worker connections are available to handle the client’s request, you will get the “worker connections are not enough” error.
However, you can modify this value to the maximum amount of memory available on your server to avoid the error. For that, execute the following command.
trendoceans@linux:~$ ulimit -n
1024As you can see, the maximum number of memory on my server is 1024, which I can use to increase the size of the worker connections.
Now, open your NGINX configuration file using your choice of text editor.
trendoceans@linux:~$ sudo vim /etc/nginx/nginx.confAnd update the worker_connections directive value from 768 (maybe different in your case) to 1024 (depending upon your memory limits) value.
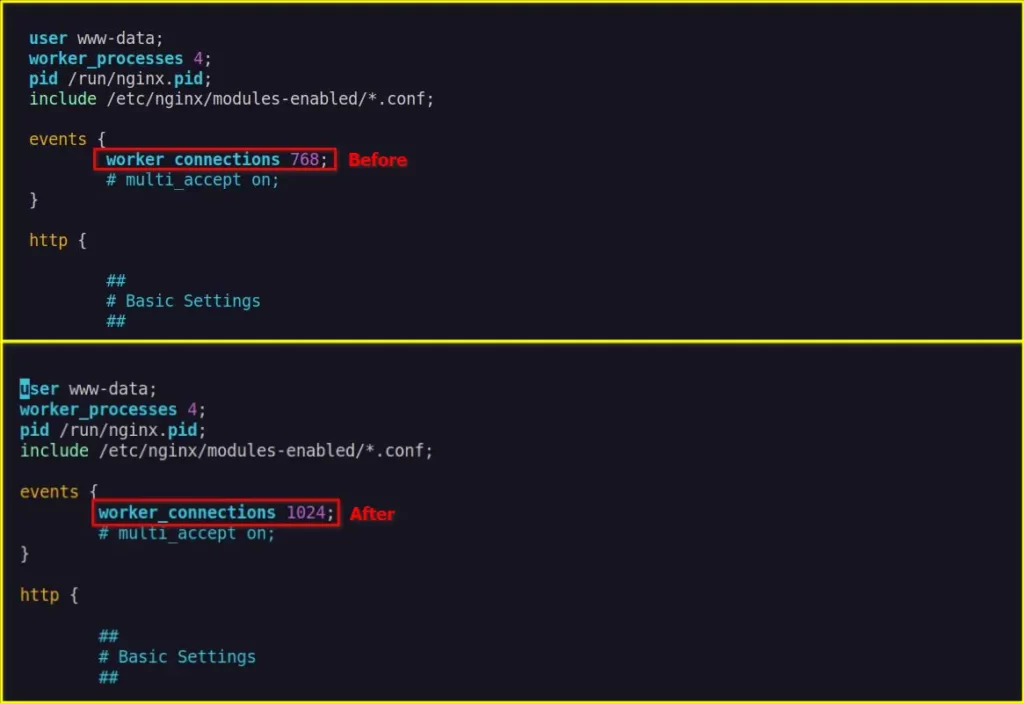
If the traffic limits reach a maximum of 1024 memory (or clients), then you need to modify your server size and increase the worker_connections directive value accordingly to your new server size.
Restart the NGINX Server
After making all the changes, execute the following command to check the syntax of your config file is updated without any errors.
trendoceans@linux:~$ sudo nginx -tIf there are no errors, then run the following command to restart your NGINX server.
trendoceans@linux:~$ sudo systemctl restart nginxWrap Up
I hope this article is helpful for you. However, if you still have any confusion between the worker_processes and worker_connections directives.
Then let me give you a simple example: if you are running worker_processes 1 with worker_connections 768, then you will only be able to serve 768 clients at one time.
However, if you are using worker_processes 2 with worker_connections 768, then you are able to serve 1536 clients. Using this method, you can find the maximum number of clients you can serve from your server.
max_clients = worker_processes * worker_connections
If you get the “worker connections are not enough” error, then you can increase the worker_processes or worker_connections values depending on your server size.
If you are using the maximum resources, then you need to upgrade your server hardware to increase the size of your worker_processes and worker_connections.
That’s all you need to understand. I tried to make it as simple as I could. Still, if you have any questions or queries, feel free to ask them in the comment section.