PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor. It is one of the oldest server-side programming language used to create Dynamic and Responsive Web-App.
The most popular CMS and frameworks like WordPress, Magento, Joomla, Drupal, and Laravel are written in PHP Language.
In this guide, we will cover on how to Install PHP on Ubuntu 20.04 or 18.04 with the Apache and Nginx web-server.
Table of Contents
What we will cover
- Install PHP 7.4 with Apache on Ubuntu.
- Install PHP 7.4 with Nginx on Ubuntu.
- Install PHP extension or modules.
- Run PHP File.
Install PHP 7.4 with Apache on Ubuntu
If you need to install PHP 7.4 with Apache webserver, you can easily Install it from the Ubuntu repositories using the following commands:
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php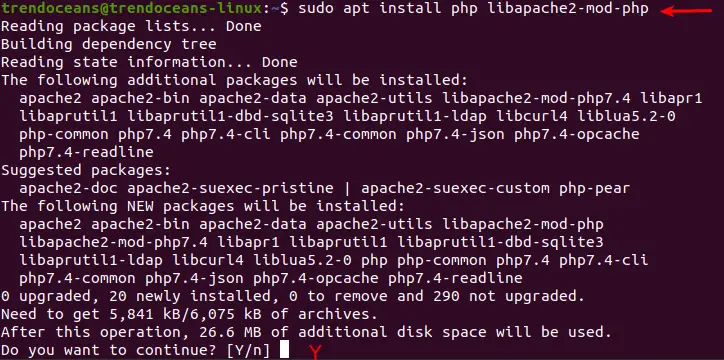
To verify whether PHP is installed in your system, with the PHP version check command:
$ php -V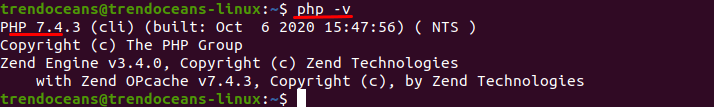
After the package gets installed, you need to restart the Apache server with the command:
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2Install PHP with Nginx on Ubuntu
When you want to Install Nginx over the Apache server, you can follow the simple steps.
Before Installing Nginx, make sure to remove Apache2 from your Ubuntu System to avoid any clashes:
Remove Apache 2 from Ubuntu
To remove Apache from Ubuntu pass the set of command in your Terminal
Step 1. First step is to stop Apache service:
$ sudo systemctl stop apache2.serviceStep 2. In this step we will purge and autoremove to apache2:
$ sudo apt purge apache2
$ sudo apt autoremoveAfter completing the above step, we can Install Nginx on Ubuntu follow the steps.
Install Nginx on Ubuntu
To Install Nginx you can download from the Ubuntu Official repository or You can Install from the Source file.
In this instance, we will Install Nginx using the simple command:
$ sudo apt install nginx
After that, you need to start the Nginx server while Installing Nginx to start type:
$ sudo systemctl start nginx.service
$ sudo systemctl status nginx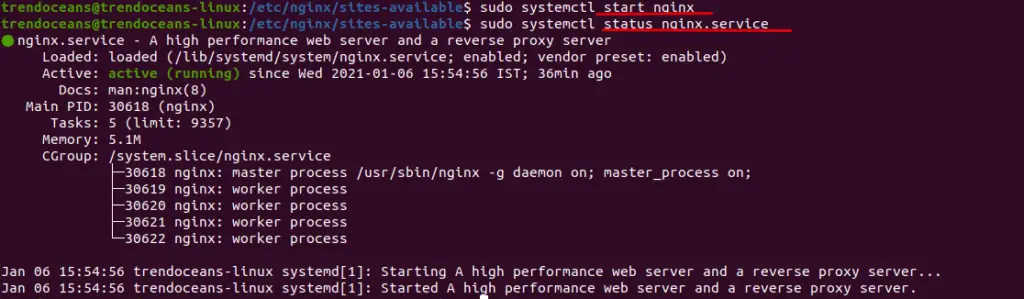
Nginx is installed in your Ubuntu System, and We will Install PHP with the FPM package:
$ sudo apt install php-fpm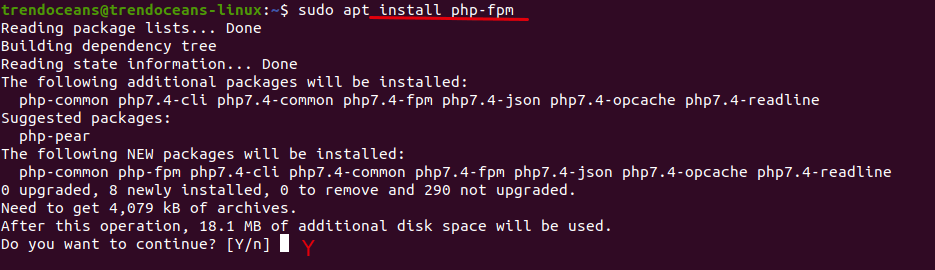
If your thinking about why we are Installing FPM (FastCGI process manager) module with PHP. The reason is simple Nginx directly cannot process the PHP file. So, we to Install fpm manually with PHP to process the file.
Configure Nginx Default
To process PHP file in Nginx web-server you need to configure “default” Config file.
Open your terminal and type or do-copy paste the following command:
$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/defaultIn this file, you need to uncomment a few lines as per the below screenshot and save the file.
With Comment
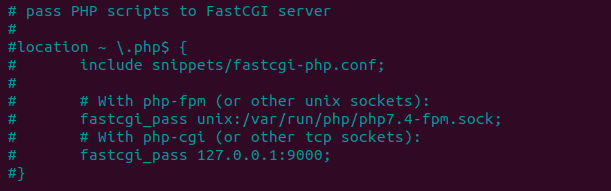
After Uncomment
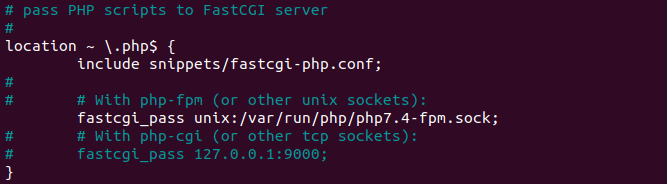
A last step is to restart the nginx and php7.4- fpm with following command:
$ sudo systemctl restart php7.4-fpm
$ sudo systemctl restart nginxInstall PHP extension or modules
From all the above steps, we know How to Install PHP with Apache and Ngnix.
This is the optional step If you want to Install Major modules that Larvel servers require, such as
$ sudo apt install php7.4-common php7.4-bcmath openssl php7.4-json php7.4-mbstringFor any-other module you can refer to documentation.
Run PHP file on Ubuntu
All the above we have configured the webserver now it’s time to run to PHP file. Before that, we need to create a PHP file In the “/var/www/html” directory.
Open terminal and type the following code
$ sudo nano /var/www/html/demo.php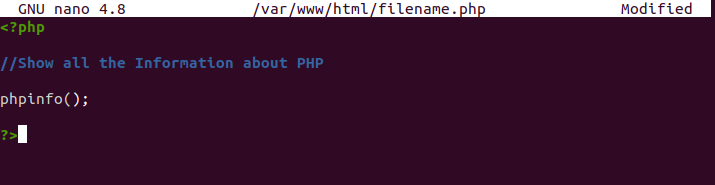
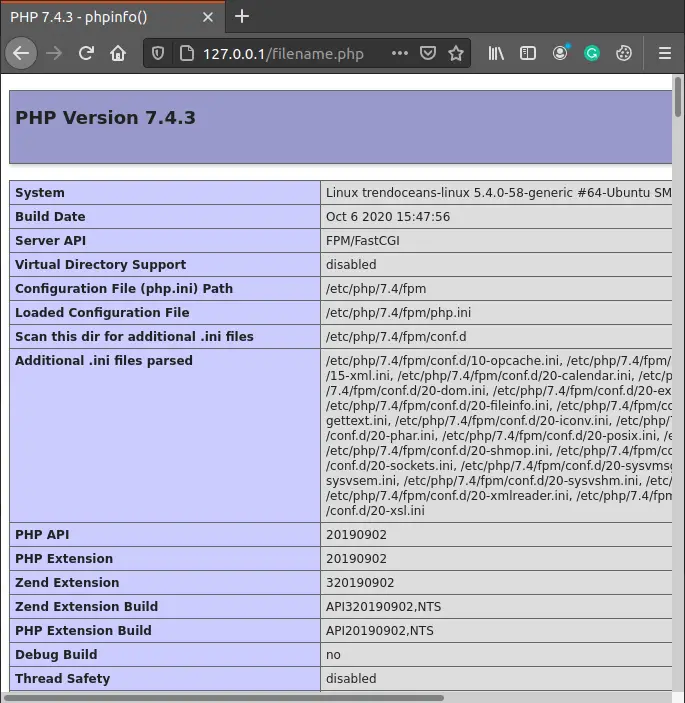
Save and close the file and Open the Web-Browser and type your IP address or http://localhost/ with the filename.php
In my case, I have run a PHP file on my local computer So, I have typed the localhost address with the PHP filename.
We have use the function phpinfo() to get the PHP configuration of my web-sever.
Wrap Up
That’s it to Install PHP on Ubuntu with Apache or Nginx server. If you are stuck somewhere or need any assistance, please comment down.
If you want to install PHP using the XAMPP server on Your Ubuntu Machine, Click on Learn more.

A man with a tech effusive who has explored some of the amazing technology stuff and is exploring more. While moving towards, I had a chance to work on Android development, Linux, AWS, and DevOps with several open-source tools.